risk of high blood pressure
- Genetic predisposition. People with high blood pressure in first-degree relatives (father, mother, grandmother, grandfather, siblings) are at higher risk. The more close relatives with high blood pressure, the greater the risk;
- Aged over 35 years old;
- Stress (stress-induced hypertension) and mental stress. The stress hormone adrenaline increases your heart rate. It immediately constricts blood vessels;
- taking certain medications, such as oral contraceptives and various dietary supplements (iatrogenic hypertension);
- Bad habits: smoking or drinking. Components of tobacco can cause vasospasm - the involuntary contraction of blood vessel walls. This narrows blood flow;
- Atherosclerosis – plaque clogging blood vessels. Total blood cholesterol should not exceed 6. 5 mmol/L;
- Kidney failure (renal hypertension);
- Endocrine disorders of the adrenal gland, thyroid, or pituitary gland;
- Too much salt in food. Table salt can cause arterial spasms and become lodged in the body;
- Inactive. Lack of physical activity causes a slow metabolism and gradually weakens the entire body;
- Being overweight. Each additional kilogram increases blood pressure by 2 millimeters of mercury - mmHg;
- Sudden changes in weather;
- Chronic sleep deprivation and other "aggressors".
- low (risk less than 15%);
- average (15% to 20%);
- High (more than 20%);
- Very high (more than 30%).
High blood pressure 1 degree

- "soft" or light;
- medium or marginal;
- Very severe or isolated contractions.
Symptoms of stage 1 hypertension
- Headache worsens with exercise;
- Pain or tingling on the left side of the chest, radiating to the shoulder blade and arm;
- Black spots appeared in front of my eyes.
Complications of grade one hypertension
- nephrosclerosis - hardening of the kidneys;
- Hypertrophy of the heart muscle (left ventricle).
Treatment of stage 1 hypertension
High blood pressure 2 degrees
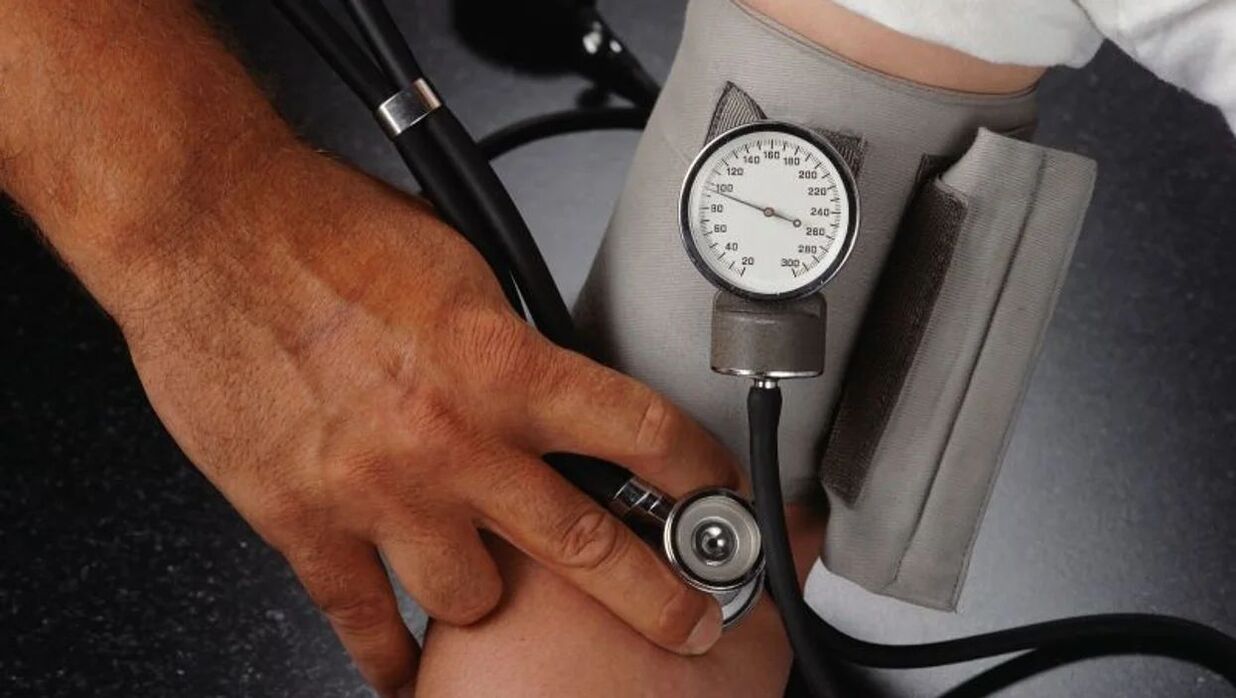
Symptoms of stage 2 hypertension
- pulsating sensation in head;
- Hyperemia - overflow of blood vessels, such as redness of the skin;
- Microalbuminuria – the presence of albumin in the urine;
- numbness and coldness in the fingers;
- fundus lesions;
- Hypertensive crisis - a sudden increase in pressure (sometimes up to 59 units at a time);
- The emergence or worsening of signs of target organ damage.
- Autonomic (increased heart rate, excessive excitement, hand tremors, unmotivated panic, dry mouth);
- Edema (drowsiness, swelling of eyelids, suppressed consciousness);
Second degree complications of hypertension
- Bleeding occurs in various organs because the blood vessel walls become thicker, lose elasticity and become brittle. Increased blood flow can easily damage these blood vessels. As an aneurysm develops, the opposite process occurs. Here, due to increased blood circulation, the walls become stretched and thinned. They are very fragile and tear easily.
- Pathologically narrowed lumens increase the likelihood of atherosclerosis (fatty deposits on tube walls) and thrombosis (blockage with blood clots). Bleeding of brain cells can lead to death from lack of oxygen. This phenomenon is called encephalopathy. Ischemia is a lack of oxygen to the heart. Angina is persistent chest pain.
Hypertension secondary disability

- Medical history information regarding hypertensive crisis;
- Patient working conditions.
- Strong vibration and noise are prohibited;
- No overtime, weekend or night work is allowed without the employee's consent;
- No sustained physical or psycho-emotional stress is allowed;
- It is prohibited to work at high altitudes, in hot workshops, or near dangerous machinery;
- Reduce work hours that require high levels of concentration;
- Seven-hour working day.
- Men over 60 years old;
- Women over 55 years old;
- People with irreversible anatomical defects.
Treatment of stage 2 hypertension
High blood pressure 3 degrees

Symptoms of stage 3 hypertension
- Impaired motor coordination;
- persistent visual impairment;
- Paresis and paralysis caused by cerebral circulation disorders;
- Prolonged hypertensive crisis with speech impairment, confusion, and severe heart pain;
- The ability to move, communicate and care for oneself independently is severely limited.
Complications of grade 3 hypertension
- Myocardial infarction – the muscularis layer of the heart;
- Cardiogenic asthma - choking attacks;
- Peripheral artery injury;
- Hypertensive retinopathy affects the retina of the eye;
- A scotoma ("darkness") is a defect, a blind spot in the field of vision.
Hypertension disability level 3
Treatment of stage 3 hypertension
High blood pressure 4 degrees
Example of risk calculation based on stage of hypertension
| high normal | Level 1 | level 2 | Level 3 | ||
| Garden 130-139 Diastolic blood pressure 85-89 |
Garden 140-159 Diastolic blood pressure 90-99 |
Garden 160-179 Diastolic blood pressure 100-109 |
Systolic blood pressure ≥180 Diastolic blood pressure ≥110 |
||
| Phase I | No other FR | low risk (Risk 1) |
Low risk (risk 1) | medium risk (Risk 2) |
high risk (Risk 3) |
| 1-2 Frontline | low risk (Risk 1) |
medium risk (Risk 1) |
ease / high risk |
high risk (Risk 3) |
|
| ≥3FR | short / medium risk (Risk 1) |
ease / high risk |
high risk (Risk 3) |
high risk (Risk 3) |
|
| second stage | POM, CKD grade 3 or DM None organ damage |
ease / high risk |
high risk (Risk 3) |
high risk (Risk 3) |
High / very high risk |
| The third phase | Establish CVD, CKD stage ≥4 or diabetes with organ damage |
Very high risk (Risk 4) |
Very high risk (Risk 4) |
Very high risk (Risk 4) |
Very high risk (Risk 4) |
SBP - systolic blood pressure
DBP - diastolic blood pressure
Radiofrequency is a risk factor
CKD - chronic kidney disease
DM - diabetes
POM - target organ damage
- Obesity (BMI over 30), and central or visceral obesity, which is determined by waist circumference.
- Social isolation.
- Chronic stress.